Payments cascading: how it improves transaction success rates
.jpg)
.jpg)
False declines are silent revenue leaks. Each blocked authorisation is a lost order today and a dent in lifetime value tomorrow.
You don't have to accept that loss. Cascading payments provide every transaction with a controlled second chance without disrupting the checkout flow.
In this article, we'll cover what cascading payments are, how they work, the benefits and challenges, and how Corefy helps you put cascading into action.
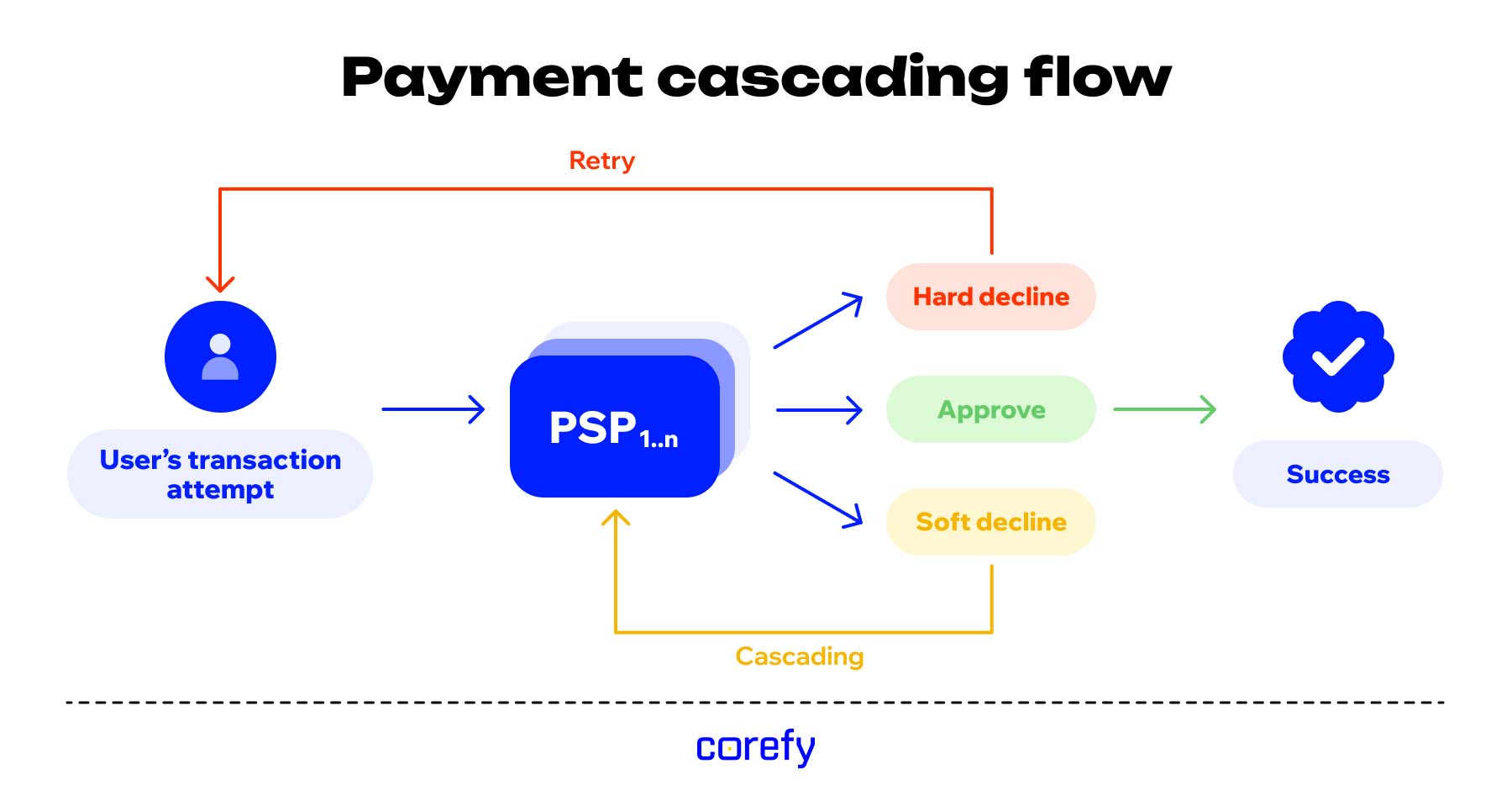
Payment cascading is a payment processing technology that automatically routes declined transactions through multiple payment gateways or processors until successful approval is achieved.
Сascading payments are the key to rescuing transactions that would otherwise fail. To the user, it feels like a single seamless payment without re-entering card details; under the hood, your system is finding a route that works.
False declines are among the costliest issues in payments – 41% of customers will never shop with a company after a declined payment. This can mean lost revenue and damaged trust.
Cascading of payments offers a smarter safeguard. Instead of abandoning the transaction, the system retries it through another provider – increasing the approval rate without introducing checkout friction.
Payments cascading automatically passes a declined transaction to another payment processor, following a pre-set order, to give each payment multiple chances to succeed without asking the customer to try again.
Here’s what happens in the background:
When we began working with a PSP client, their conversion rate sat at just 56.2%. A significant portion of lost sales stemmed from failed or expired transactions – a clear signal that friction in the payment flow was costing them revenue.
To solve this, we implemented smart routing and cascading payments. Instead of ending the journey at the first failure, the transaction automatically cascades to a fallback provider, giving it another chance to succeed and keeping the customer in the flow.
Within a year, their payment conversion rate jumped to 85.1%. Failed transactions fell sharply, as cascading and retry logic significantly reduced payment interruptions.
Smart routing and cascading often work together, but solve different parts of the problem:
Used together, payment routing ensures each transaction is processed in the optimal way from the start, while cascading retries recoverable declines to reduce failed payments further.
Retries occur when the issue is on the user's side – for example, insufficient funds or an incorrect CVV – and the customer can manually try again, perhaps using a different card or payment method.
Cascading kicks in when the failure comes from the provider’s side, for instance, when a transaction is wrongly declined due to overly strict risk scoring or fraud filters. Another provider might approve the same payment without issue, and cascading ensures it gets that second chance automatically.
Here's how payment processing changes before and after cascading implementation:
| Aspect | Without cascading | With cascading |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction success rate | A single failure often means a lost payment | Multiple fallback paths maximise approval rates |
| Customer experience | Failed payments frustrate shoppers and cause drop-offs | When a provider declines, the system reroutes the payment instantly and seamlessly for the customer |
| Revenue impact | False declines directly cut into revenue | More approved payments mean more revenue |
| Operations | Users unable to complete a payment often reach out to support or operations repeatedly | Cascading works automatically in the background |
| Continuity | Gateway outages disrupt payments | Automatic failover maintains uptime |
Implementing cascading pays off, but it’s not plug-and-play. Businesses face 5 key hurdles:
Payment orchestration platforms like Corefy simplify cascading by handling complexity behind the scenes:
Payment cascading is a strategic way to recover failed transactions and boost approval rates.
Its full impact comes when it’s managed through orchestration – making it easier to configure, monitor, and scale across multiple PSPs.
Payment cascading is especially important for merchants and fintech services that manage high transaction volumes, global operations, or experience frequent payment declines. It offers a strategic edge for:
By using cascading processors, you improve reliability, reduce false declines, and maintain a smooth customer experience – without asking the user to try again.
Cascading may occasionally route a payment to a higher-cost provider to secure approval. While this might slightly increase the fee for a single transaction, smart rules and analytics within the software help optimise the balance between cost and success rate. By automatically retrying failed payments and reducing the volume of payment failures, merchants can minimise revenue losses.
Start with a payment orchestrator that offers broad processor coverage and a single, unified API. Look for built-in analytics to monitor performance and fine-tune routing, along with baked-in PCI DSS compliance to reduce your security workload. The right partner should simplify integration, automate retry logic, and offer ongoing support – all to help you recover more payments and drive higher approval rates with less manual effort.