Payment routing 101: definition, process, rules, and workflow
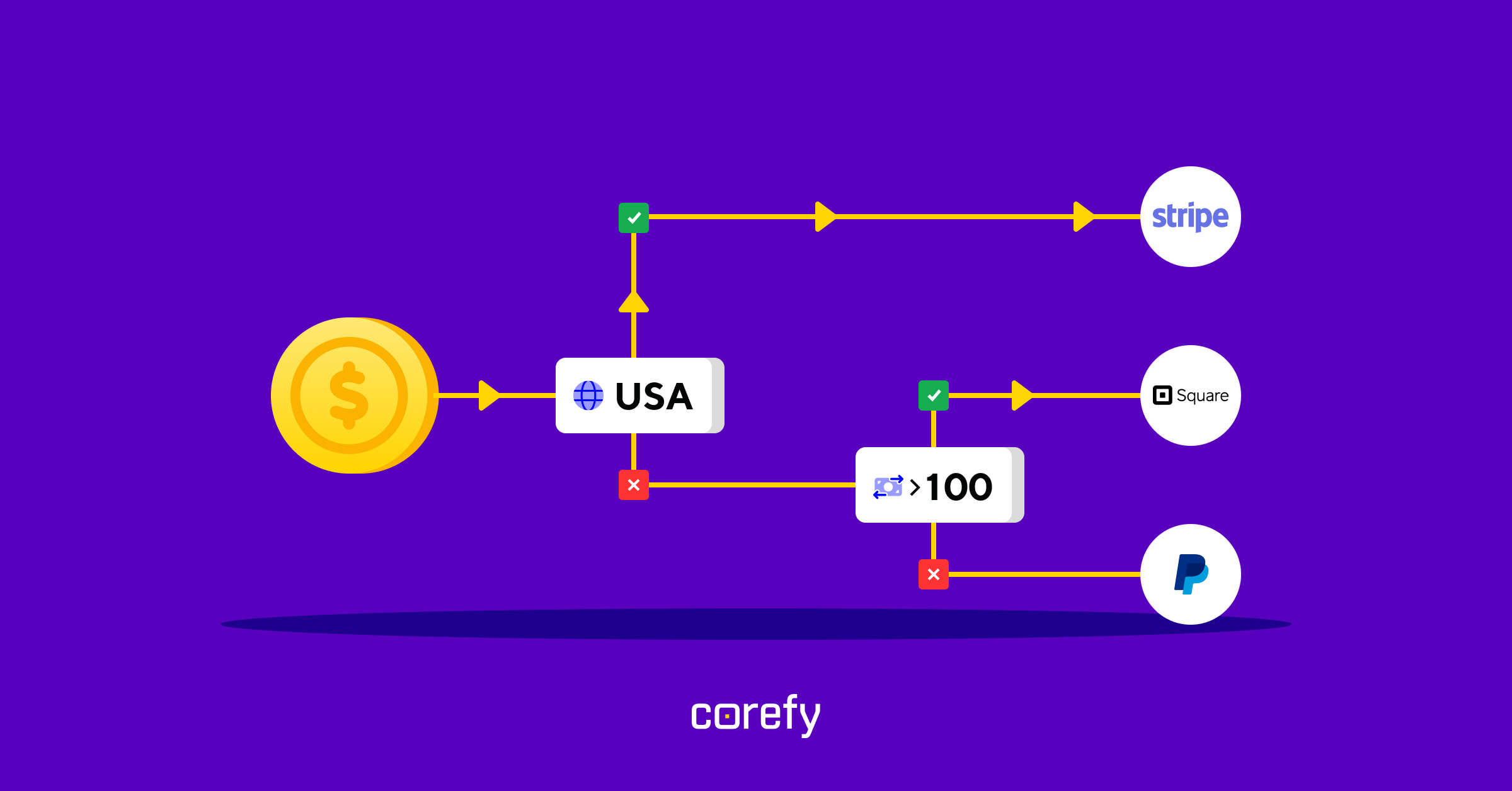

This is an ultimate guide to payment routing, covering everything from basics to expert tips on configuring your own routing scheme. Read it, share with colleagues, or bookmark it for later — this resource is carefully crafted and regularly updated for you.
Payment routing is a core smart payment processing function that determines the best path for each transaction in real time. Instead of sending payments to a single gateway, it evaluates multiple acquiring banks, payment processors, and service providers, then routes the payment to the one most likely to succeed.
This 'behind-the-scenes' logic uses predefined rules and dynamic data points such as card type, issuing bank, currency, transaction value, location, or historical provider performance. The goal is to increase the chances of approval while balancing cost, speed, and reliability. In practice, routing is typically paired with a customisable white-label gateway on the front end, so merchants can keep the checkout experience consistent while the routing logic runs in the background.
For the customer, the intelligent payment routing process is invisible — they simply complete their purchase. For the business, however, it’s a powerful optimisation lever. By implementing smart routing, companies can:
In the early days of online payments, most merchants depended on a single acquiring bank or gateway. This setup left them exposed: when the acquirer had downtime, enforced strict risk rules, or lacked regional coverage, transactions failed. Cross-border payments were especially unreliable, and merchants had almost no ability to optimise outcomes.
As e-commerce grew, businesses started connecting to multiple PSPs and acquirers to build redundancy. But routing logic was still static and often hard-coded by developers, such as sending all Visa traffic to one provider and Mastercard to another. This added resilience but lacked agility. Updating rules required engineering time, and failures still meant lost revenue.
The breakthrough came with dynamic or intelligent payment routing. Instead of relying on fixed paths, routing engines began evaluating each transaction in real time, taking into account factors like issuer country, card brand, currency, transaction amount, risk score, and historical approval rates. This data-driven approach made it possible to send every transaction to the provider with the highest chance of success, improving acceptance rates and lowering costs.
Today, with AI and machine learning, routing engines can learn from billions of transactions. They can adapt to issuer behaviour, reroute instantly when a provider goes down, and balance between conversion uplift and cost efficiency. For industries with high payment volumes, like iGaming & betting, routing has evolved from a back-office function into a direct driver of profitability.
There are two primary ways businesses can route transactions: static and dynamic payment routing. Let's compare these options.
| Feature | Static routing | Dynamic routing |
|---|---|---|
| Routing method | Fixed, pre-defined paths (manual setup) | Real-time decisioning based on rules and data |
| Flexibility | None — same provider for every matching case | High — adapts to acquirer performance, market, or risk signals |
| Approval rates | Can drop sharply if provider underperforms | Optimised by selecting provider with best chance of success |
| Failure handling | No fallback — failed transactions are lost | Automatic retries and failover to alternative providers |
| Cost efficiency | May result in higher fees due to suboptimal routing | Routes to lowest-cost acquirer or most favourable conditions |
| Technical upkeep | Hardcoded logic, developer effort required for changes | Rules managed via dashboard, updated instantly |
| Use cases | Suitable for small merchants with low volumes and limited geographies | Essential for global, high-volume merchants seeking conversion lift |
Bottom line: Static routing is a basic safety net, while dynamic routing is a revenue-optimising growth lever. For most businesses working with multiple providers, moving from static to dynamic routing is a must.
The payment routing workflow decides which provider should process each transaction to maximise its chance of success. Instead of sending all payments through one fixed path, a routing engine analyses transaction details in real time and selects the optimal provider based on a set of rules and live conditions.
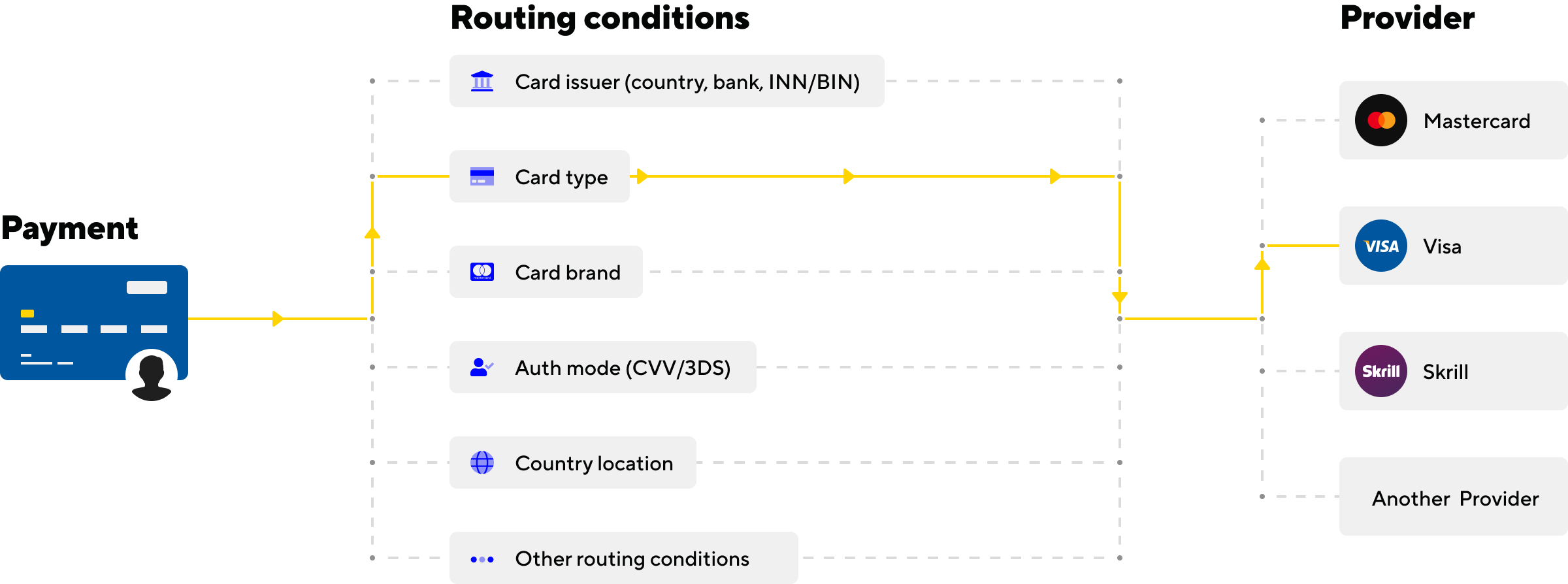
Here’s how the payment routing process unfolds:
When a customer submits their payment, the system captures multiple data points:
This context acts as the foundation for routing decisions.
The payment gateway routing engine then applies predetermined rules or algorithms to evaluate the best available path. For instance, route payment made with a European-issued Visa card to a local EU acquirer to avoid cross-border scrutiny, direct a high-value transaction to a provider with stronger fraud checks, or choose the lowest-cost processor for low-margin payments.
Once the most suitable provider is selected, the transaction is routed to them for authorisation. The provider then passes it through the relevant card network or payment scheme to the issuing bank.
If the first attempt fails, whether due to strict risk filters or technical issues, the system immediately attempts cascading. This means rerouting the transaction to a secondary provider, chosen either by predefined order or by live performance data. Smart retry strategies can recover up to 20-30% of initially declined payments.
Advanced setups don’t stop at fixed rules. They use historical payment routing data and real-time monitoring to refine decisions constantly, learning which providers perform best for specific card types, markets, or times of day. This turns transaction routing into a continuous cycle of analysis, decisioning, execution, and optimisation — all happening invisibly to the customer, who only sees a smooth checkout and a successful payment.
Let’s take a closer look at how to route payments for your business.
Start by connecting all the merchant accounts you hold with different PSPs. With Corefy, this takes just a few clicks and entering your accounts’ credentials in the dashboard.
Then, define the payment routing logic that reflects your business priorities, whether that’s lowering processing costs, boosting approval rates, managing risk, or balancing traffic. With your goals in mind, you can build a routing scheme that turns them into actionable rules and workflows.
A routing scheme is a decision tree that defines which route a transaction takes. It consists of conditions, branches, and strategies that reflect your business logic. In short, it sets the rules for selecting routes based on the payment’s context.
At Corefy, you can build routing schemes either in a visual editor or a JSON editor, depending on your preference.
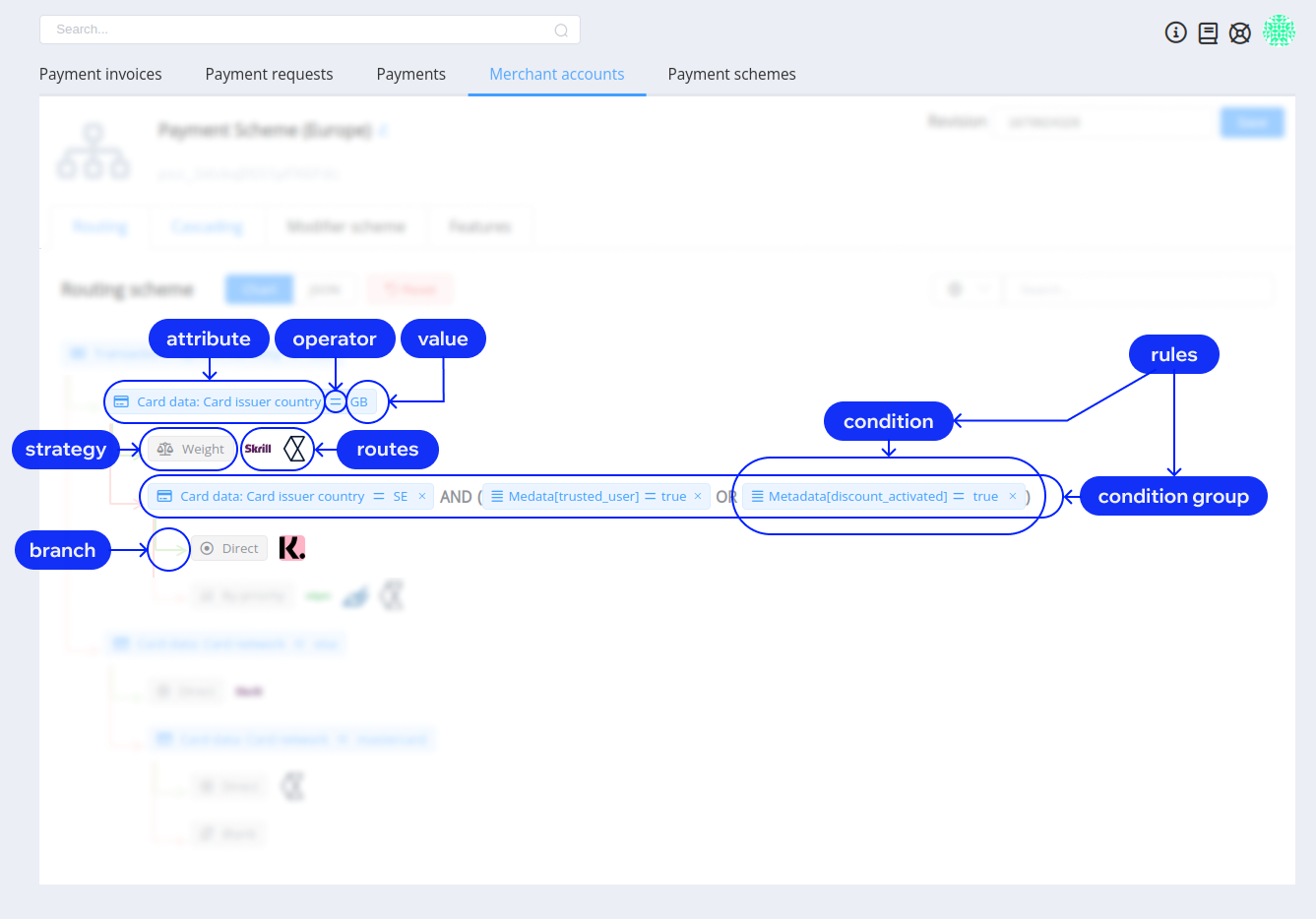
Every scheme starts with conditions — payment routing rules or sets of rules. A simple condition might look like: ‘Issuer country is the UK’. A more complex set of conditions could be: ‘Issuer country is the UK’ AND ‘Transaction amount is greater than £100’.
Each condition is made up of three elements:
Every condition has two branches: a positive one, triggered when the condition is met, and a negative one, triggered when the condition isn’t met. Each branch can lead either to another condition for further refinement, or directly to a strategy, which determines the actual payment route.
Once a transaction reaches the end of a branch in your routing scheme, a strategy determines how the final payment route is chosen. Think of routing strategies as the ‘decision method’ that translates your business logic into action.
Here are the strategies Corefy offers:
By combining these strategies with conditions and branches, you can design routing schemes that reflect your business goals, whether it’s maximising approval rates, cutting processing costs, testing new providers, or controlling risk exposure.

As you scale, routing logic often grows from a handful of basic rules into a sophisticated web of interdependent conditions. Managing that complexity efficiently requires more than simple rule-setting. That’s why we offer an advanced toolkit to help you maintain full control while automating the decisions that don’t need human input.
Modifiers let you fine-tune authentication and risk logic directly within your routing flow. For example:
These micro-adjustments ensure every payment meets the right balance between security, cost-efficiency, and conversion.
Even with the most optimised routing logic, occasional provider timeouts or issuer declines are inevitable. Corefy’s cascading feature keeps your revenue safe by automatically retrying failed transactions with alternative providers according to your pre-set scheme. You define the order, conditions, and retry logic — the system handles the execution in milliseconds.
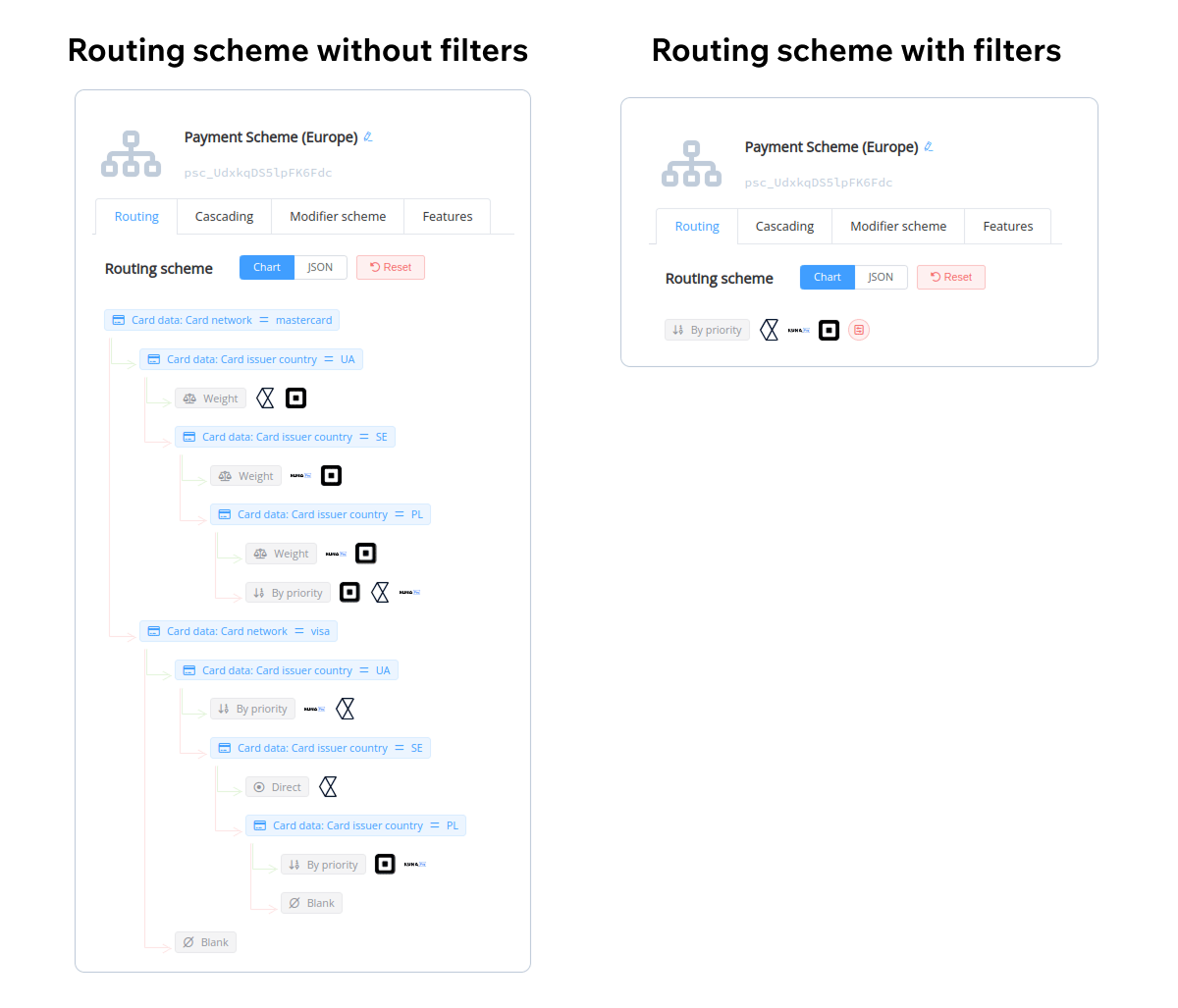
Routing filters bring structure to large, data-heavy routing setups. Instead of managing long lists of manual rules, you can create filters based on transaction attributes, such as country, currency, payment method, BIN range, or customer segment.
Once filters are in place, Corefy automatically channels each transaction through the right path. For instance, payments from European cards can be directed to local acquirers, while recurring subscriptions can be routed to PSPs with higher recurring approval rates. This approach not only declutters complex schemes but also enhances flexibility — you can update a filter once, and the change applies across all relevant routes.
Global intelligent payment routing system helps merchants working in a multi-provider setup address four main challenges:
Payments routing is not a silver bullet. Implementing and managing it comes with real challenges that businesses should weigh carefully.
If you are a high-risk business and your conversion rates are suspiciously low, check out this case our team solved recently.
To address the issue, we thoroughly examined the client's routing scheme and analysed the reasons behind transaction declines. We discovered that a significant portion of declines was attributed to fraud and restrictions imposed by acquirers on transactions from certain countries. It became evident that there was a lack of effective communication between the client and their providers regarding the specificities of high-risk acquiring and anti-fraud systems.
On behalf of the client, we took the initiative to contact their providers and gather detailed information about the restrictions applicable to high-risk merchant accounts. It turned out that transactions originating from certain regions using specific cards were prohibited.
With this knowledge in hand, we assisted our client in creating a new routing scheme that focused on parameters such as ‘user IP’ and ‘issuer country’. This allowed us to minimise failures by directing each payment to the most suitable provider that accepted such transactions. Additionally, we implemented a cascading feature, providing each transaction with an extra opportunity for successful processing.
Thanks to these strategic improvements, our client experienced a remarkable turnaround, with the conversion rate exceeding 60%.
Payment routing is a strategic lever that directly impacts your revenue, approval rates, and customer experience. By applying data-driven logic instead of static rules, you can make every transaction count, reducing declines and processing costs while keeping operations stable across providers and regions.
However, building and maintaining intelligent routing on your own can be complex and time-consuming. That’s why many businesses rely on Corefy’s industry’s best payment routing engine. Our platform gives you the tools to design, test, and optimise routing schemes effortlessly, and our team supports you every step of the way. Together, we translate complex payment logic into measurable business outcomes.
Routing rules define how you direct each transaction across payment providers. Well-configured payment routing instructions ensure that every transaction takes the path most likely to succeed — based on card type, region, and historical provider performance. This intelligent approach to routing payments reduces false declines and improves approval rates, helping businesses recover otherwise lost revenue. Try Corefy’s ROI calculator to estimate the possible positive effect of routing and other payment orchestration features on your business.
Corefy’s routing engine goes beyond basic setups or direct card routing. It lets you create, test, and adjust payment routing options without code, combining real-time data with flexible business rules. You can easily build customisable payment routing schemes, including cascading and retry logic, and manage your entire payments flow routing from a single dashboard. With 100+ routing attributes, including metadata, you receive unmatched flexibility to optimally cover your business logic.
To start using a payment routing engine, you need to have active merchant identification numbers (MIDs) with your payment providers. Once that’s in place, you can integrate a payment orchestrator like Corefy via API and instantly access its full toolkit and network of 550+ ready-made integrations. After connecting, simply enter your MID credentials into Corefy’s dashboard to link your providers. From there, you can configure your payment routing scheme — defining rules for how transactions are directed across gateways, acquirers, and methods. Our team of payment experts will guide you through every stage of the process, from onboarding and setup to optimisation and scaling, ensuring you reach your business goals efficiently and confidently.
Data is at the heart of effective payment routing. It powers routing decisions by analysing issuer performance, success rates, and decline codes. Continuous monitoring helps fine-tune your routing logic and keep every payment on the most efficient path. In short, strong data turns routing payment transactions into a measurable competitive advantage.
Tracking these metrics helps businesses optimise routing for payment processing and continuously improve their payments performance: